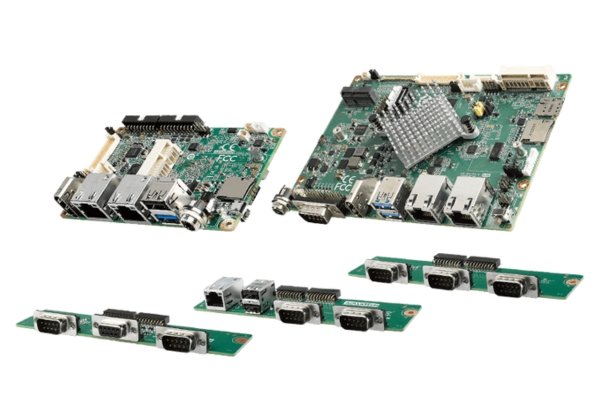
Technology is getting smaller, faster, and more efficient. Behind many of today’s smart machines and connected devices is a tiny but powerful component the SBC motherboard.
Also known as a Single-board computer, this compact hardware packs all the essential parts of a computer onto one board. It includes the processor, memory, storage, and input/output interfaces all in a single unit.
What makes it stand out is its ability to run specific tasks with minimal power, size, and cost. That’s why it’s become a popular choice in embedded systems like industrial machines, smart home devices, kiosks, and IoT solutions.
Whether you’re building a custom automation setup or upgrading your hardware infrastructure, understanding what an SBC motherboard does can help you make smarter decisions.
At Global Infotech Solutions, we help businesses choose and implement reliable SBC-based solutions for various industries. Let’s take a closer look at what makes an SBC so essential in embedded environments and how it could be the right fit for your next project.
What Is an SBC Motherboard?
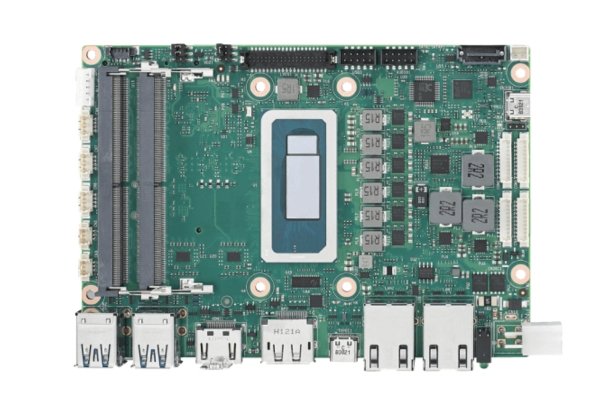
An SBC motherboard, short for Single-board computer motherboard, is a complete computer built onto a single circuit board. That means the CPU, RAM, storage, input/output ports, and even network interfaces are all included in one compact unit.
Simple Explanation:
Think of it as a mini-computer that doesn’t need extra parts to work. Unlike traditional desktops or laptops that use separate components (motherboard, processor, RAM, hard drive), an SBC combines all of them into one ready-to-use board.
These boards are small, powerful, and energy-efficient, making them perfect for machines and devices that need to run specific tasks like collecting sensor data or controlling motors without needing a bulky setup.
SBC Motherboard vs Traditional Motherboard
| Feature | SBC Motherboard | Traditional Motherboard |
| Size | Very small | Large |
| Integration | All-in-one | Needs external components |
| Power Consumption | Low | Higher |
| Customization | Limited | Very flexible |
| Target Use | Embedded systems | Personal computers/servers |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Moderate to High |
How Does an SBC Work in Embedded Systems?
Before we dive into this, let’s quickly understand what embedded systems are.
Embedded systems are specialized computer systems that are built to perform a single or limited set of tasks. These could be anything from controlling the temperature in a smart fridge to monitoring real-time data in an industrial robot.
Now here’s where the SBC motherboard steps in.
How It Functions:
- Central Control Unit: The SBC acts as the brain of the embedded device.
- Real-Time Processing: It processes data from connected sensors or devices and takes action instantly.
- Low Power Use: Because they are compact and built for specific tasks, SBCs use very little electricity.
- No Need for External Add-ons: Most SBCs come with everything onboard saving space and reducing complexity.
Real-World Example:
Imagine a vending machine that accepts digital payments and sends alerts when stock is low. The entire system can run on an SBC motherboard handling everything from the display to the payment gateway.
Types of Single Board Computers
Single-board computers come in various types, depending on the hardware architecture and intended use.
Popular Types:
1. ARM-based SBCs
- Low power usage
- Often used in mobile devices and IoT products
- Example: Raspberry Pi
2. x86-based SBCs
- Compatible with standard PC software
- Suitable for more complex embedded applications
- Common in industrial PCs
3. GPU-powered SBCs
- Designed for tasks that require graphics processing or AI capabilities
- Used in surveillance, robotics, and edge computing
Use-Based Categories:
- Consumer SBCs: Low-cost boards for hobby projects or learning
- Industrial SBCs: Rugged boards built for 24/7 operation in factories or automation setups
Advantages of Single Board Computers in Embedded Use
Here are the main reasons Single Board Computers are a smart choice in embedded environments:
Compact Size
- Takes very little space
- Can be easily mounted in small devices
Lower Power Consumption
- Consumes minimal electricity
- Ideal for solar-powered or battery-based systems
All-in-One Solution
- No need to add external components like CPU or memory
- Saves design and assembly time
Cost-Efficient
- Cheaper than building systems with separate hardware
- Great for mass production
Fanless Operation
- Most SBCs are passively cooled
- No moving parts = longer lifespan and quiet performance
Reliable
- Fewer connectors mean fewer failure points
- Stable in extreme environments
Perfect for Automation and IoT
- Easily integrates with sensors, motors, and displays
- Commonly used in smart homes, factories, and security systems
Common Use Cases of SBC Motherboards
You’ve probably interacted with SBCs without even realizing it. They’re used in everyday devices as well as advanced systems.
Real-World Applications:
- Home Automation Systems: Controlling lights, doors, and appliances
- Digital Signage and Kiosks: Touchscreen display units
- Medical Equipment: Patient monitors, infusion pumps
- Industrial Automation: Robotic arms, assembly lines
- Retail Systems: POS terminals, barcode scanners
- Security Devices: Surveillance cameras, alarm systems
- Smart Farming: Weather sensors, irrigation control
- Automotive Systems: Navigation, infotainment, driver alerts
In all of these, the SBC motherboard plays the role of the central processing unit, quietly powering the operation.
How to Choose the Right SBC Motherboard
If you’re planning to build or upgrade an embedded system, picking the right SBC is a key step.
Here’s what you should consider:
- Purpose
What exactly will the SBC do? Basic control or heavy processing? - Processor Type
ARM for energy saving, x86 for complex operations - RAM and Storage
Higher specs are needed for video processing or data-heavy tasks - Connectivity Options
Look for USB, Ethernet, Wi-Fi, GPIO pins, etc. - Operating System Support
Linux, Android, Windows IoT – depending on your software stack - Environmental Tolerance
Choose fanless or rugged designs for tough conditions - Budget and Scalability
Balance cost with performance and future upgrades
SBC vs Traditional Motherboard: What’s the Difference?
This is a common question. Here’s a simple breakdown:
| Feature | SBC Motherboard | Traditional Motherboard |
| Purpose | Specific tasks | General computing |
| Components | All-in-one | Modular, separate parts |
| Power Need | Very low | High |
| Size | Small | Large |
| Upgrades | Limited | Easily upgradeable |
| Cost | Affordable | More expensive |
SBCs are ideal when you need focused performance in a small space, like a kiosk or a smart device.
Why SBC Motherboards Are the Future of Embedded Design
The demand for connected devices and intelligent automation is growing rapidly. SBC motherboards are making that shift possible.
As industries shift to leaner, faster, and more efficient systems, SBCs offer the perfect combination of:
- Performance
- Size
- Cost-effectiveness
At Global Infotech Solutions, we help engineers and businesses find the right SBC solutions for embedded applications from concept to integration.
Whether you’re working on a smart kiosk or an industrial controller, the SBC motherboard is your reliable building block.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is an SBC motherboard used for?
Answer: SBC motherboards are used in systems that require compact size, low power usage, and reliable performance. Common applications include IoT devices, industrial machines, medical monitors, smart displays, and automated systems.
Q2. Can SBCs replace normal motherboards?
Answer: Yes, in many cases. For embedded systems or machines that perform a fixed task, SBCs are a better choice. However, for desktops and gaming PCs, traditional motherboards are still required due to their flexibility and upgrade options.
Q3. Are SBCs good for industrial applications?
Answer: Absolutely. Many industrial automation setups rely on rugged SBCs that can operate in extreme temperatures, handle vibrations, and run continuously without failure.
Q4. Which is better: Raspberry Pi or industrial SBC?
Answer: Raspberry Pi is great for learning and prototyping. But for real-world applications where reliability and long-term supply are important, industrial SBCs are the better option.
Q5. Do SBCs support Windows or Linux OS?
Answer: Most SBCs support Linux-based systems like Ubuntu or Debian. Some higher-end SBCs also support Windows 10 IoT or Android, depending on the hardware.
Conclusion
The SBC motherboard may be small, but its impact is huge. From smart devices to factory automation, SBCs are powering the next generation of embedded technology.
They offer a perfect balance of simplicity, efficiency, and performance, making them ideal for systems where space and power are limited but reliability is crucial.
If you’re planning to build, upgrade, or deploy embedded systems, explore SBC options that match your needs.
Global Infotech Solutions can help you choose the right board, integrate it into your project, and build a reliable embedded setup without unnecessary complexity.

